What are engineering plastics?
Engineering plastics can be used as engineering materials and plastics that replace metal in manufacturing machine parts. Engineering plastics have excellent comprehensive properties, such as high rigidity, low creep, high mechanical strength, good heat resistance, and good electrical insulation. They can be used for a long time in harsh chemical and physical environments. They can replace metals as engineering structural materials, but they are more expensive and have smaller output.
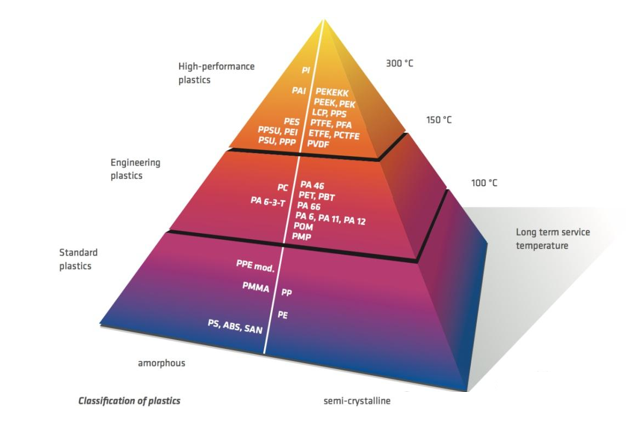
Its characteristics are: plastic with long-term heat resistance temperature above 100℃, tensile strength above 50MPa, and bending elasticity modulus above 2.4GPa.
Development history of plastics:

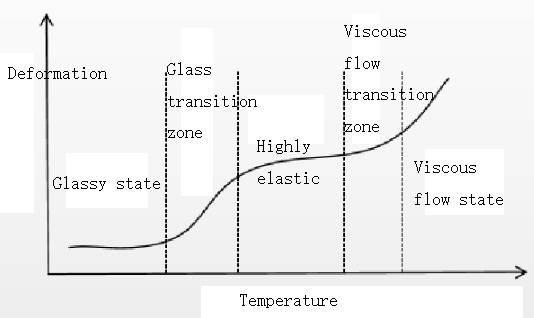
Crystalline plastics and amorphous plastics
Plastics with high crystallinity are crystalline plastics, and attraction between molecules easily interacts with each other to become strong plastics.
Crystallization refers to regular arrangement of molecules, which becomes a crystal structure after cooling. Crystalline structure of general plastics is a collection of many linear, elongated polymer compounds. Degree to which molecules are arranged in a regular manner is called degree of crystallization (crystallinity). It also means that each molecule is only arranged in order, so crystalline resin is actually only partially crystallized. Proportion of crystalline parts is crystallinity.
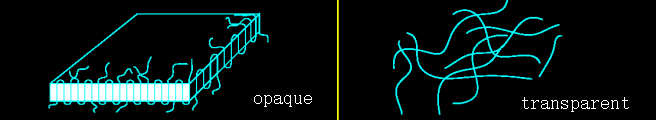
| Semi-crystalline materials | Amorphous materials |
| Opaque | Transparent |
| Both Tg point (glass transition temperature) and Tm point (melting temperature) exist | Only Tg point |
| 1. Resistance to chemicals 2. Wear resistance 3. High liquidity 4.High hardness 5. High heat resistance 6. Flexibility 7. Adding reinforced materials to quickly improve mechanical and thermal properties | 1. Can be transparent 2. Good toughness 3. The size is stable 4.Low warpage 5.Easy to color 6. High temperature dependence during processing 7. Low shrinkage |
Classification of plastics
Comparison of physical properties of commonly used plastics
| PBT PET | PC | m-PPO | PA6 PA66 | POM | |
| Lightweight | △ | ○ | ● | ○ | × |
| Formability | ○ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ |
| Finished product shrinkage | ○ | ● | ● | ○ | ○ |
| Water absorbency | ● | ● | ● | × | ○ |
| Hot water resistance | × | ○ | ○ | △ | ○ |
| Impact strength | ○ | ● | ○ | ● | ○ |
| Dimensional stability | ○ | ● | ● | △ | ● |
| Solvent resistance | ● | × | △ | ● | ● |
| Weather resistance | ○ | ○ | ○ | △ | × |
| Flame resistance | ○ | ● | ● | ○ | × |
| Electrical | ● | ● | ● | ○ | ○ |
| Wear resistance | ○ | △ | △ | ● | ● |
●: Best; ○: Better; △: OK; ×: Bad.
Comparison of chemical resistance of commonly used plastics
| PBT PET | PC | m-PPO | PA6 PA66 | POM | |
| Weak acid | ● | ● | ○ | ○ | △ |
| Strong acid | △ | △ | ○ | × | × |
| Weak base | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | △ |
| Strong base | × | × | ○ | ○ | × |
| Reactive gas | ○ | ○ | × | △ | △ |
| Oil | ● | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Acetone | ○ | × | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Benzene | ○ | × | × | ● | ○ |
| Carbon tetrachloride | ● | × | × | ○ | ● |
| Alcohol | ● | △ | ○ | △ | ● |
| Esters | ○ | × | × | ● | ○ |
| Gasoline | ● | × | △ | ● | ● |
●: Best; ○: Better; △: OK; ×: Bad.
Heat resistance and price comparison of various engineering plastics

How to distinguish composition of engineering plastics
· IR (infrared absorption spectrum) – determine formula of plastic
Organic compounds contain some specific functional machines that often absorb infrared rays of a specific wavelength. Irradiate an organic sample with infrared rays, measure and record infrared rays and resonance absorption absorbance of different wavelengths of sample, and obtain absorption spectrum of organic matter, thereby determining composition of plastic.
· DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimeter) – Determine Tg and Tm of plastics
Use heating to gradually heat up plastic in instrument; because plastic molecular bonds need to absorb heat to break at glass transition temperature Tg and melting point Tm, different wave peaks will be seen in graph. (You can also see purity of material)
· TGA (thermal gravimetric analysis) – determine composition and ratio of plastics
By using heating method, combustion temperature and percentage of each component in material can be analyzed at different temperatures, then its composition and addition ratio can be determined.
Common testing equipment for engineering plastics
| Mass spectrometer (GC MASS) | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) | Infrared spectrometer (IR) |
| Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) | Embrittlement temperature testing machine | Constant temperature and humidity machine |
| Dielectric strength tester | Melt flow index meter | Flame resistance testing equipment |
| Colorimeter | Potential difference automatic titrator | Trace moisture analyzer |
| Gas Chromatograph (GC) | Universal testing machine | Weathering test machine |
| IV tester | TABER Abrasion Machine | Differential Calorimetry (DSC) |
| High temperature furnace | Arc resistance testing machine | Hydrometer |
| Hardness Tester | Dielectric constant tester | High impedance tester |
| Impact testing machine (can measure -40℃) | Thermal distortion temperature testing machine | Oxygen consumption index tester |